2025 PCI Guidelines Released: IABP Receives Authoritative Recommendations
2025-06-23
Recently, the "Guidelines for percutaneous coronary intervention (2025)" (hereinafter referred to as the "2025 PCI Guidelines"), compiled by a panel of experts organized by the Interventional Cardiology Group of the Chinese Society of Cardiology and the Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology, was officially released.

The 2025 PCI Guidelines are an update to the 2016 edition, incorporating clinical research findings from both domestic and international studies in recent years. They also reference the latest international guidelines issued by the ACC/AHA and ESC, ensuring high relevance, practicality, and authority.
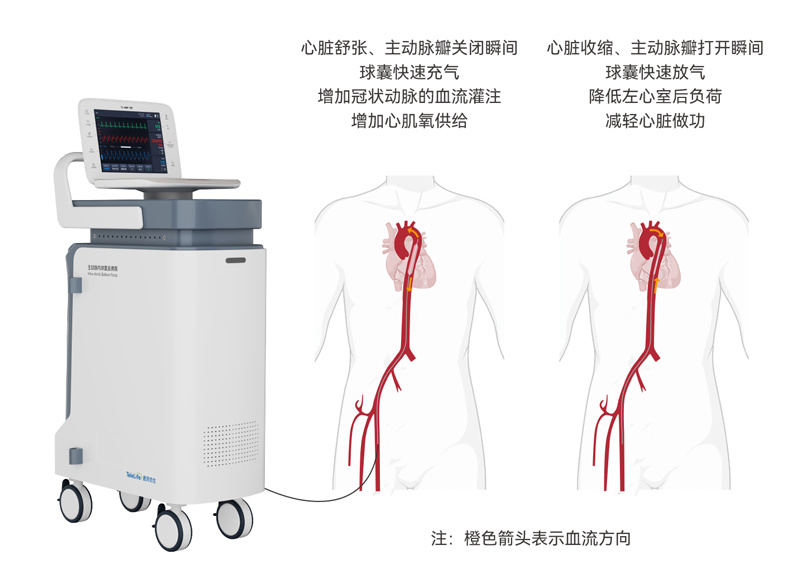
As an emergency circulatory support device, the Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) can increase stroke volume and cardiac output, enhance blood perfusion to vital organs, and reduce left ventricular afterload, thereby providing critical support during PCI procedures. The 2025 PCI Guidelines also clarify the applicable scenarios and recommendation categories for IABP, as detailed below:
For very high-risk patients undergoing PCI, such as those with cardiogenic shock, decompensated heart failure, hemodynamic instability, severe arrhythmias, or even a history of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, mechanical circulatory support devices should be routinely used (IIa, C-EO).
For STEMI patients complicated by cardiogenic shock, although international guidelines no longer recommend the routine use of IABP (III-NB, A), it should be promptly employed in cases where vasopressor therapy is ineffective, hemodynamic instability persists, or acute left heart failure occurs (I, C-EO), as its clinical efficacy is well-established. Similarly, IABP support is necessary for STEMI patients with mechanical complications who experience hemodynamic instability, cardiogenic shock, or acute left heart failure (I, C-EO).
For patients who develop hemodynamic instability due to any complications during primary PCI, IABP support should be immediately initiated (I, C-EO). Additionally, for patients with recurrent myocardial ischemia refractory to medical therapy or those with severely impaired cardiac function, IABP circulatory support should be provided during both emergency and elective PCI (IIa, C-EO) to ensure patient safety.
The Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) system can directly provide oxygenated arterial blood circulation support, reducing perioperative mortality in PCI for patients with cardiac arrest or shock, and should be used when available. However, ECMO increases left ventricular afterload and does not prioritize blood supply to the heart and brain. Combining ECMO with IABP can compensate for these limitations.

As an integrated heart failure lifecycle solutions provider, Tongling Bionic initiated the R&D of IABP at its inception. After years of dedicated research, the company launched China's first fully self-developed IABP device, the TL-IABP-100, in January 2025. Approved for market release, this breakthrough ended the long-standing monopoly of imported devices, offering hospitals and patients a more competitive new option.
Guidelines for percutaneous coronary intervention (2025)
一、Recommendation Classes
1.I: Benefits far outweigh risks—Strongly Recommended
2.IIa: Benefits outweigh risks—Moderately Recommended
3.IIb: Benefits slightly outweigh risks—Weakly Recommended
4.III-NB (No Benefit): Benefits equal risks—Not Recommended
5.III-Hm (Harm): Risks outweigh benefits—Strongly Not Recommended
二、Levels of Evidence
1.Level A: High-quality evidence derived from multiple high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or their meta-analyses, or from one or more RCTs supported by high-quality registry studies.
2.Level B-R (Randomized): Moderate-quality RCT evidence from one or more RCTs and their meta-analyses.
3.Level B-NR (Non-Randomized): Moderate-quality non-RCT evidence from one or more well-designed and executed non-randomized studies, observational or registry studies, and their meta-analyses.
4.Level C-LD (Limited Data): Evidence from randomized, observational, or registry studies with design or execution limitations, their meta-analyses, or physiological/mechanistic clinical studies.
5.Level C-EO (Expert Opinion): Expert consensus based on clinical experience.
Latest News
Great News! Tongling Bionic Wins Award
2025-11-12



